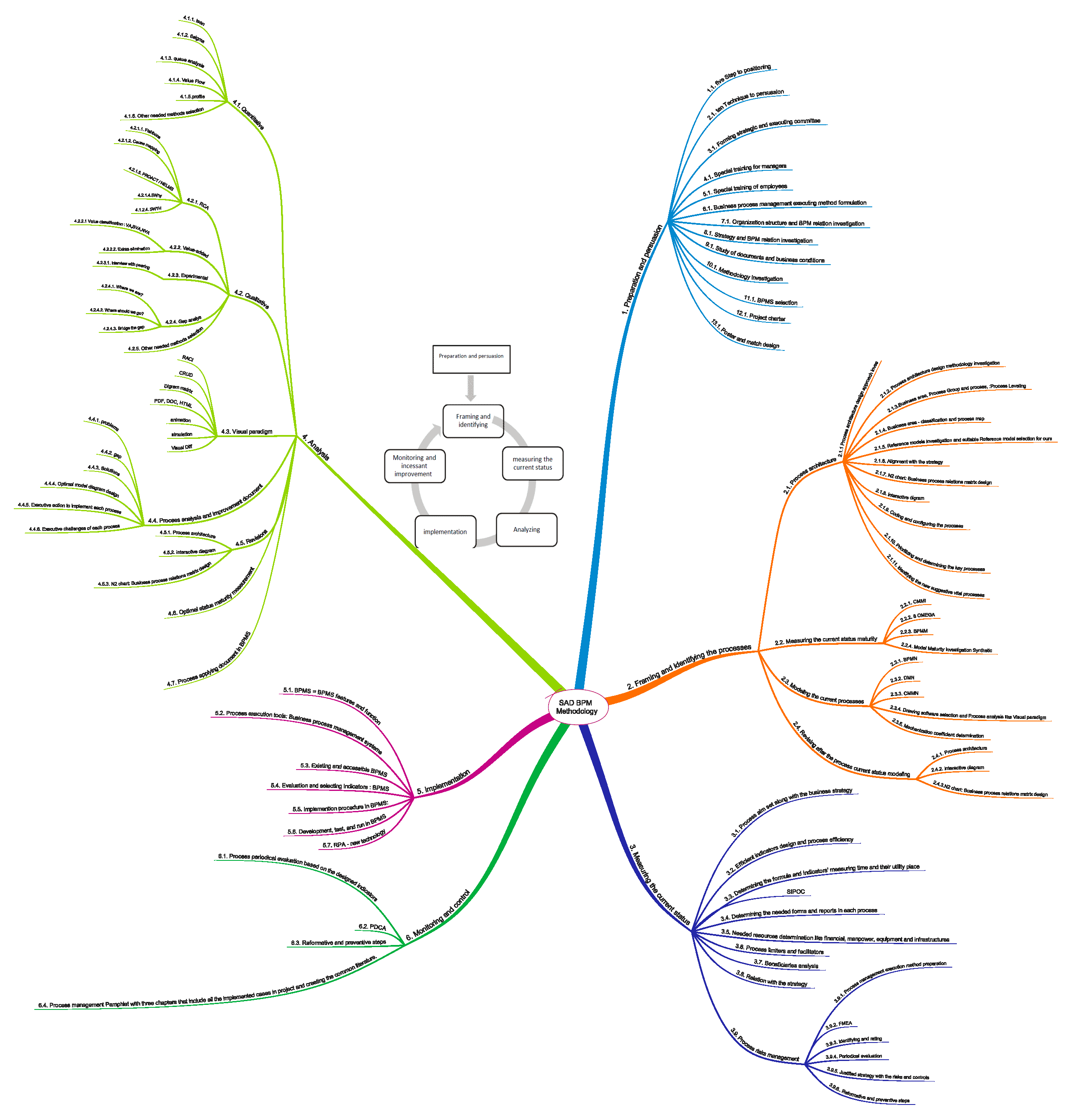
D & R BPM Methodology results from 12 years of experience in the field of processes and review and research on other methodologies. Many years of research and experience have been spent discovering a comprehensive methodology and covering all the activities involved in deploying process management. This methodology was first fully used in one holding company and at the same time in its 18 subsidiaries in 2015, and later in many other businesses and organizations, including the oil and gas industry and the food industry, and science and technology parks by the author as a project manager and manager. Over the past four years, more than 30 organizations have been trained to establish business process management in their organization through SAD BPM Methodology. In an image, this methodology has the following steps.
Preparation and persuasion
Before we start deploying BPM in the organization, we need to prepare the staff and senior managers to use this technique. New approaches and methods that extend BPM are needed to enable building complex adaptive systems that react dynamically to changes and bring order out of the chaos. (Huseyin Kir ∗, 2020).
The adoption of BPM provides organization-wide transparency and clarity, enabling previously separate business units who are responsible for different sections of work, to understand their shared relationship concerning the business processes. (Becker, 2015) In this phase, we will form executive and steering committees. We will take steps to position BPM in the organization and convince it. We will also select the BPMS tools required for use in the implementation phase in this step. To create a culture in the organization, we will teach, design a contest, design a poster, etc. We will also prepare a BPM charter to determine the scope and requirements, etc.
Also, in this phase, it is necessary to examine the relationship between BPM and strategy, organizational structure, ISO, and other quality management techniques so that we can understand its place in the organization and establish a coherent and integrated relationship between different methods and by creating a suitable platform, the organization Let us help the Almighty.
Process Framing and Identification
Enterprise engineering deals with the design of processes which aim to improve the structure and efficiency Of business organizations. It develops approaches based on modeling techniques, particularly on Business process modeling, to ensure the quality and the global consistency of enterprise strategies and Expectations (Elyes Laminea, 2020)in the first step, the scope of work is precisely defined. Processes are then identified through interviews, and process priorities are provided (process architecture design). By designing the process architecture, we will determine the process list, process hierarchy, and process relationships. Some models, such as APQC[1]-PCF[2], can be used for this purpose. We then score the list of processes based on the organization’s appropriate prioritization indicators and prioritize the processes.
In the next step, the processes are drawn in order of priority, with an interview with an expert and the study of related documents. The BPMN standard will be used to plot the process. (AS IS extraction and modeling).
In this step, be sure to design the process architecture and, in the next steps, modify it if necessary by completing the information.
Measuring the current situation
Although business process management (‘BPM’) is a popular concept, it has not yet been properly theoretically grounded. This leads to problems in identifying both generic and case-specific critical success factors of BPM programs. (Trkman, 2009). A team needs to be formed to measure selected processes’ performance by determining key performance indicators (KPIs) (process identification).
In addition to the index, stakeholders, and their requirements, SIPOC[3], the process description identify the resources required to execute the process, the limitations and facilitators of the process, and the risks of the process.
Analysis
So far, we have realized what our situation is. Now we have to do two things
- Determine our distance from the desired condition. This is called gap analysis, which can be done using the modeling technique. It is necessary to analyze the gap and measure the organization’s level of maturity to predict the next step or steps of improvement. To do this, we use different maturity models such as eight omega or CMMI.
- Identify process complications and problems. Each process may have issues in terms of time, cost, quality, or flexibility. For this analysis, root cause analysis (RCA[4]), value-added, experimental analysis, LEAN, 6 Sigma, etc., can be used.
Then we will start designing the solution according to the identified gaps and complications. These strategies will usually lead to removing an activity from a process or adding an action, or improving it in terms of tools and execution methods. In the last stage of this phase, we will design the desired situation based on the specified solutions.
Implementation
The implementation of BPM is a complex process and requires many technical and non-technical aspects. (Sharfina Febbi Handayani*, 2019). Now it’s time to run the improved model. This step is one of the most challenging activities to do and requires a lot of care. In this step, we will use BPMS to mechanize and execute processes in the organization. One of the best tools for implementation is implementing and deploying processes, BMMS, which has the latest technology with the highest BPM compliance. BPMSs reduce the cost of generating and executing changes compared to other standard methods while speeding things up.
Note:
Before entering this phase, we will prepare the process implementation document. This document has detailed and sufficiently detailed analysis as well as IT technical details to mechanize the processes.
Continuous monitoring and improvement
When the state of an internal business process is not normal or when it is not the same with a customer’s awareness, a negative value gap arises, which means the difference between service providers’ intention and service recipients’ expectation. (Chong Un Pyon, 2010).
In order to stay competitive Firms measure, monitor, and analyze their performance. Performance management systems are regularly implemented as balanced and dynamic solutions requiring considerable human and financial resources, and offering support to the decision-making process by gathering, elaborating and analyzing information. (Vesna Bosilj Vukˇsi ´ca, 2013). Business Process Management is a management approach that describes how companies can achieve efficiencies by integrating and improving their business processes and by aligning those business processes with corporate strategies and goals. Companies that routinely practice Business Process Management (BPM) are able to consistently improve on the results obtained from existing processes. (Alexievaa, 2012). The implemented process should be continuously monitored, and according to the process description, the intended corrections for further improvement and maturity of the organization should be identified. This step will always continue.
[1] American Productivity & Quality Center
[2] Process Classification Framework
[3] suppliers, inputs, process, outputs
[4] Root Cause Analysis